Hyperledger Basics
Why you should start using Kotlin for Android today?
January 4, 2019Setting up Hyperledger Fabric
July 15, 2019Hyperledger Basics
https://medium.com/@furqaan.vnurture/hyperledger-basics-48f4bf79852a
The blockchain technology is distributed in two categories: public blockchain and private blockchain. The public blockchain is named as Ethereum and the private blockchain is named as Hyperledger.
While using the public blockchain the transaction details are visible to all the connected entities. If the transaction is confidential and private, then the public blockchain cannot be used. Instead of the public blockchain, we can use the private blockchain which named as Hyperledger.
Why to use Hyperledger?
Hyperledger is an umbrella project of open source Blockchain and related tools started in December 2015 by the Linux Foundation. It permissioned blockchain, means any entity wants to join the network must have the permission. It uses the distributed ledger technology to record the transactions in the ledger.
There are many open source projects of Linux and Hyperledger is one of them.

Hyperledger initiatives are categorized in two categories:
1. Frameworks
2. Tools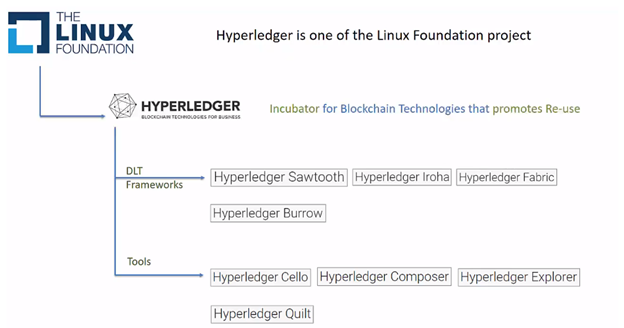
Hyperledger Frameworks
1. Hyperledger Sawtooth: led by intel
2. Hyperledger Iroha: led by Soramitsu
3. Hyperledger Fabric: IBM donated its source code for its blockchain initiatives called OpenBlockchain and that combine with source code from other partners such as Digital Assets incubated the Hyperledger Fabric
4. Hyperledger Burrow: is the most recent addition from Monax.
Hyperledger Tools
1. Hyperledger Cello: is an initiative that aims to simplify creation and management of Blockchain infrastructure.
2. Hyperledger composer: is for creating business network application using the high-level composer language.
3. Hyperledger Explorer: provides visibility to an operational Blockchain system.
4. Hyperledger Quilt: aims to achieve interoperability between different chains.
Distributed Ledger Technology(DLT):
Why to use the DLT:
Each and every industry is involved in the exchanging in some form value. For example, the retail industry is exchanging some goods for the cash. The financial industry exchanges the bonds and the stocks.
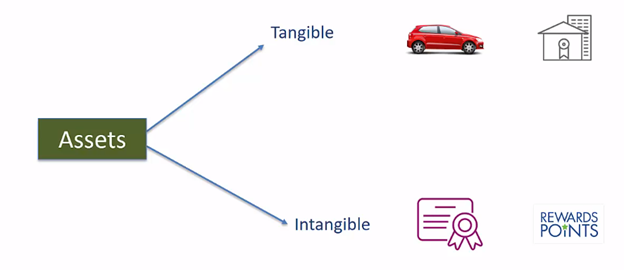
Assets
The Assets is representing the value. Assets are tangible means, we can touch it in physical world, for example car and house or Assets can be intangible, for example stock ownership certificate and reward points for the customers.
All the company must keep the tracks of all business transactions related to the Assets in a book of record also called ledger. This ledger keeps track of the exchanges happening between the businesses and other entities.
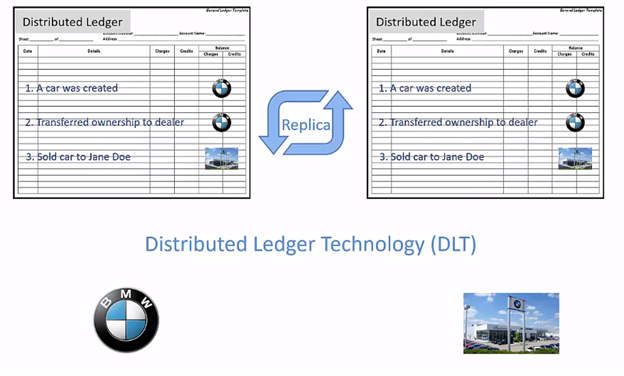
Here we are taking an example of the car company, A car manufacturing company build a car that is also an Asset. This is recorded in the ledger of car manufacturer. Now, the car company transferring the ownership of car to the car dealer, this transfer is written by car manufacturer company in its ledger.
Dealer also owns the ledgers; it also creates an entry in the ledger that it received the car ownership from manufacturer. When the dealer sells the car, the transferring of the ownership of the car from dealer to the customer is recorded in the ledger. The entities do not have visibility to each other ledger.

If we wish to find the car history, we can get the details of dealer from the car owner, the dealer can give the details of car manufacturing company from its ledger. The manufacturing company’s ledger can give us details of all the parts used in a car. The things get complicated when the car is sold to multiple owners by way of sales. The customer does not have any ledger to record the sales details.
Here distributed ledger technology come into the picture, each entity involves in the exchange in the values is having a copy or replica of the Distributed Ledger. All transactions are recorded by various entities in this distributed ledger.
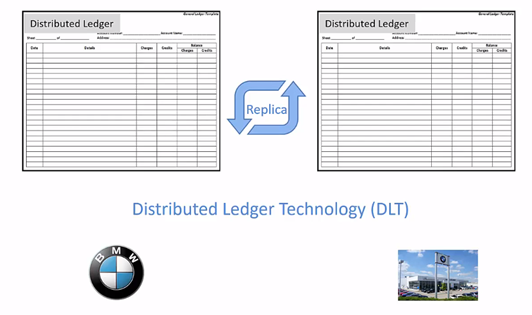
The transaction of the car manufactured is recorded not only in the car manufacturer’s company distributed ledger, but it is also reflected in the dealers distributed ledger. The same way transfer of car ownership from the dealer to the customer is recorded by the dealer and car manufacturer company’s distributed ledger.
Challenges:
Consistency: Maintain consistency across the copy of the ledgers that is all participant must see the same data in the transactions and all the transactions are always in the right order .
Privacy: participant’s may not want their identities to be disclosed. The DLT technology provide some way to manage that aspect.
Confidential: it refers to how only the authorize parties can have visibility into the transactions
The other challenges are Standardization, Interoperability, Scalability
Hyperledger Fabric: Fabric is a DLT framework that addresses most of the typical challenges associated with realization of architecture that leverages distributed ledgers.